FIND YOUR FIT AT FOOTHILLS FAST
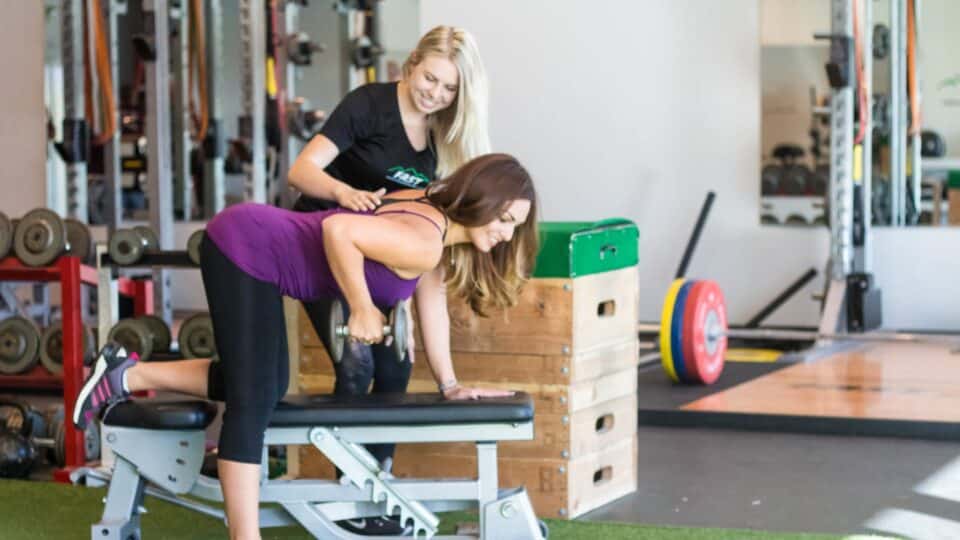
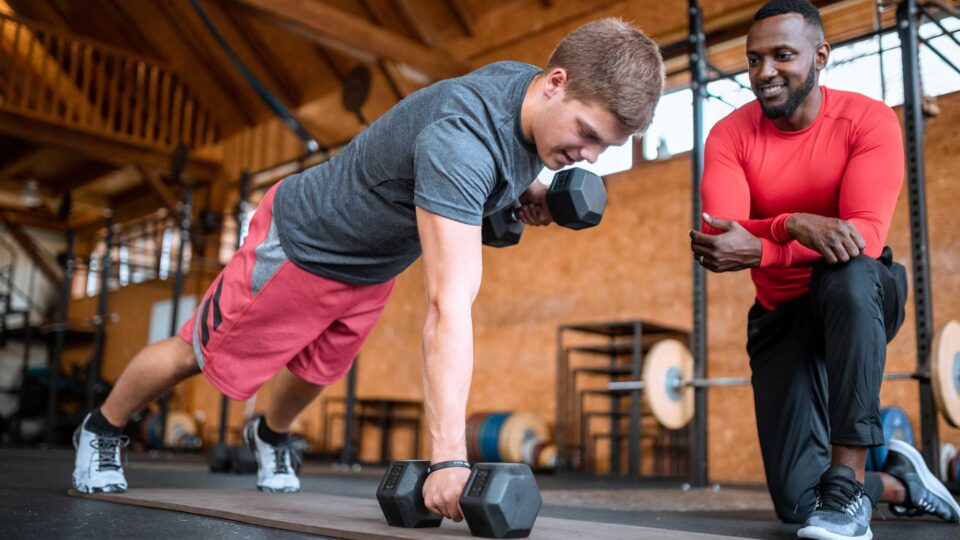
FAST is a division of Foothills Sports Medicine Physical Therapy and was developed in 2003 after recognizing that many patients were looking to maintain an active lifestyle once their physical therapy treatment was completed. With customized workouts tailored to your budget and fitness level, FAST personal trainers have the expertise to get you up and on your way to achieving your fitness goals—FAST!
GET STARTED
YOUR FIRST WORKOUT AND ASSESSMENT IS FREE!
Your first workout is on US! Meet one-on-one with our Certified Strength and Conditioning Specialists, who will assess your current fitness levels, define objectives and create a personalized program to help you achieve your goals.
HEAR FROM OUR CLIENTS
"Kyle has created very sport specific training plan for my daughter to help build functional strength and speed. Having a structured strength training program that is balanced to prevent injuries is critical for all young athletes."
Donald S. - Client at FAST Glendale
"My son and I have been working with Kyle for over a decade now! That is how amazing he is at what he does….he has clients for life. If you’re looking for a place that can adapt to your abilities, your strengths and weaknesses and build a health program tailored to your needs, this is the place!"
Bill O. - Client at FAST Glendale
"The personal trainers here are fun, friendly and possess a wealth of experience and knowledge. Our sessions are always individualized to how we feel that day. We feel lucky to have found such a great place to workout."
- Sue M. - Client at FAST Ahwatukee
2 LOCATIONS IN ARIZONA